A severe SQL Injection vulnerability was discovered in the widely-used WordPress plugin “Tutor LMS”, leaving websites vulnerable to potential data breaches. The vulnerability, an authenticated SQL Injection flaw, could have allowed attackers with subscriber or higher-level access to extract sensitive information from the site’s database, including password hashes.
The vulnerability was discovered and reported by Muhammad Hassham Nagori, a Pakistani security researcher, through the Wordfence Bug Bounty Program during their second Bug Bounty Extravaganza on February 15, 2024. Nagori’s diligence and responsible disclosure were rewarded with a bounty of $625.00.
Wordfence, a company dedicated to securing the WordPress, promptly notified the plugin developers, Themeum, on February 22, 2024. Themeum responded swiftly, acknowledging the report the following day and working on a fix. On March 11, 2024, the patched version 2.6.2 of the Tutor LMS plugin was released, addressing the critical vulnerability.
The vulnerability, assigned CVE-2024-1751 and scored a high 8.8 on the CVSS scale, stemmed from insufficient escaping and preparation of user-supplied parameters in the plugin’s Q&A questions query functionality. This oversight allowed authenticated attackers to inject malicious SQL queries, potentially leading to data extraction from the database.
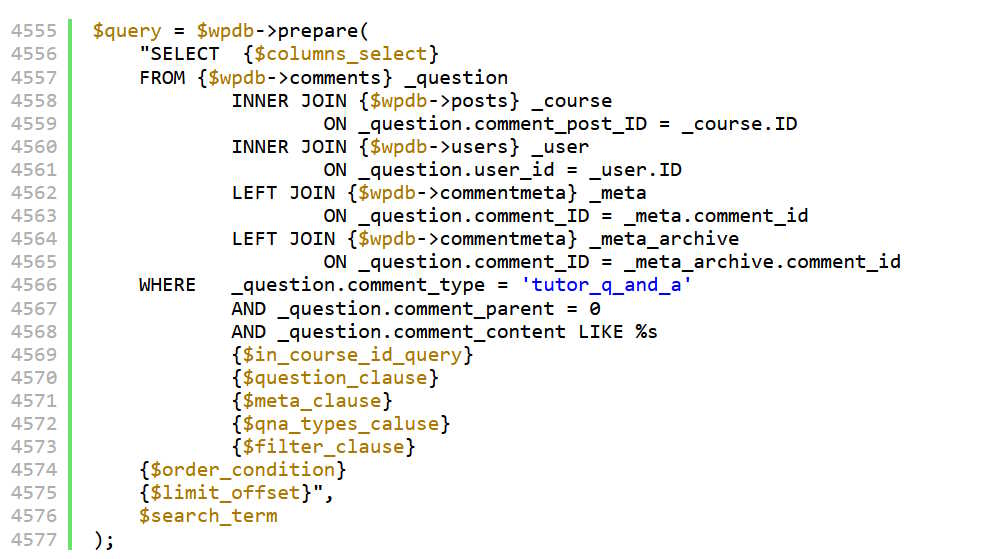
Wordfence’s technical analysis revealed that the vulnerability resided in the get_qa_questions() function of the Utils class, which failed to properly sanitize the ‘question_id’ parameter. While some instances did sanitize the input, others did not, leaving the door open for exploitation through Time-Based Blind SQL Injection attacks.
WordPress site owners using the Tutor LMS plugin are strongly advised to update to version 2.6.2 as soon as possible to mitigate the risk of potential data breaches. Wordfence commends Themeum for their prompt response and timely patching of the vulnerability, ensuring the security of thousands of websites relying on their plugin.












