Last month, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) discovered it had been hacked, forcing it to take two key computer systems offline.
The vulnerabilities exploited by the hackers were found in virtual private networking (VPN) software made by Ivanti. Specifically, the flaws being leveraged were CVE-2023-46805, CVE-2024-21887 and CVE-2024-21893 affecting Ivanti Connect Secure and Ivanti Policy Secure VPN gateways.
These vulnerabilities allowed the threat actors to gain initial access by stealing user credentials from the Ivanti devices. From there, they could move laterally and expand their access, achieving full domain compromise in some cases according to CISA.
One of the affected systems is used by federal, state, and local officials to share tools for assessing cyber and physical security risks.
The other compromised system contains data on security assessments of chemical facilities across the United States. Dealing with both cyber threats and risks to physical infrastructure, these are obviously critical systems that handle highly sensitive information.
According to CNN, the breach had “limited” impact since only those two systems were affected. The agency says it quickly took the vulnerable systems offline to contain the incident. Still, the fact that USA’s leading cybersecurity agency was successfully hacked is certainly an embarrassing situation and highlights how no organization is completely safe in today’s cyber landscape.
The vulnerabilities exploited by the hackers were found in VPN software from Ivanti. For weeks, CISA had been warning organizations to update their Ivanti software due to these flaws being actively targeted. Among the threat groups taking advantage were reportedly Chinese government hackers engaged in cyber espionage operations.
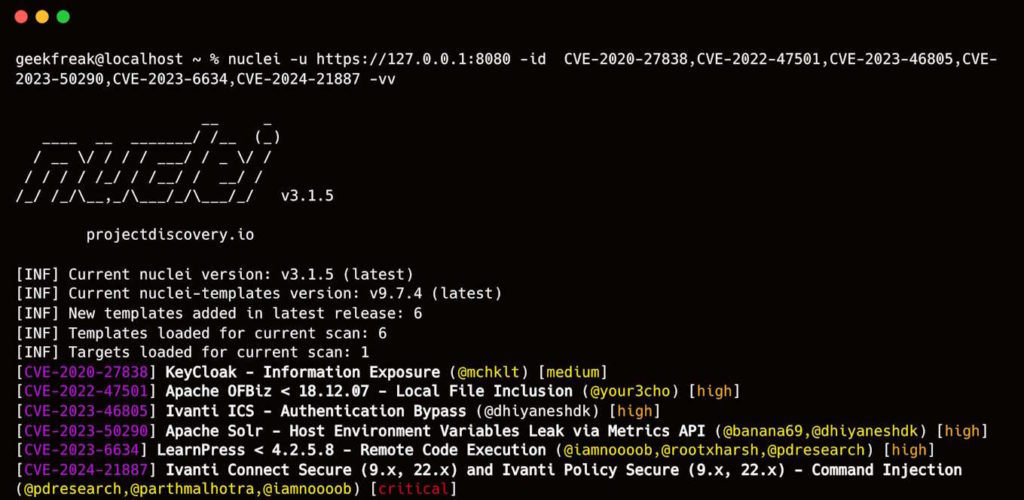
To help security administrators detect and scan for these vulnerabilities, ProjectDiscovery has released updates to their open-source Nuclei scanner to specifically scan their infrastructure check if their Ivanti VPN gateways are vulnerable to CVE-2023-46805, CVE-2024-21887.